Table of Contents
Levantine Arabic for Language Learners
Introduction
Levantine Arabic, a fascinating dialect full of history and culture, is your gateway to the Middle Eastern world. Known for its melodic tones and rich vocabulary, this dialect brings you closer to the heart of the Levantine region. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the many facets of Levantine Arabic, offering insights and practical tips for language enthusiasts and learners.
Levantine Arabic, spoken across Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, and Palestine, is more than just a means of communication. It is a reflection of the region’s diverse cultural heritage and historical depth. Whether you’re a traveler, a professional, or a curious learner, understanding Levantine Arabic can open up new worlds and opportunities.
This guide will take you through the essence of Levantine Arabic, its variations, and benefits, and offer practical advice for mastering this beautiful dialect. By the end, you’ll be ready to begin your own Levantine Arabic learning adventure.
Understanding Levantine Arabic
Definition and Scope
Levantine Arabic, or Shami Arabic, is an umbrella term for a broad dialect cluster within the Arabic language. It is primarily spoken in Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, and Palestine. Each of these regions adds its unique flavor to the dialect, making it a rich and diverse linguistic tapestry.
Levantine Arabic encompasses various local dialects spanning from the Mediterranean coast to the deserts of Jordan. Despite regional differences, speakers across the Levant understand each other thanks to shared linguistic roots and cultural ties.
Historical Background
The origins of Levantine Arabic can be traced back to ancient times when various Semitic languages influenced the region. Over centuries, the dialect evolved, shaped by interactions with Greek, Roman, Persian, and Ottoman civilizations.
Historical events played a significant role in the development of Levantine Arabic. The spread of Islam, the Crusades, and the Ottoman Empire’s rule introduced new vocabulary and expressions. These influences combined to create a dialect that’s uniquely Levantine, brimming with history and cultural heritage.
Linguistic Features
Levantine Arabic stands out for its distinct phonological characteristics. For example, the letter “qaf” (ق) is often pronounced as a glottal stop or a “g” sound, depending on the region. This phonetic variation adds a musical quality to the dialect.
The vocabulary of Levantine Arabic is a blend of classical Arabic roots and borrowed words from Turkish, French, and English. Common phrases like “shu” (what) and “kif” (how) are widely used, making conversations lively and engaging.
Grammar in Levantine Arabic is simpler compared to Modern Standard Arabic (MSA). Sentence structures are more flexible, allowing for a more conversational tone. This makes it easier for new learners to grasp and use in everyday interactions.
In Levantine Arabic, the rules are less rigid, and there is a greater emphasis on spoken language rather than written forms. Pronouns and verb conjugations often take on more straightforward forms, and the vocabulary used tends to bemore practical and relevant to daily life. Additionally, Levantine Arabic incorporates a number of loanwords from other languages, reflecting the region’s diverse cultural influences.
Because of these characteristics, learners often find studying Levantine Arabic less intimidating and more engaging. The dialect is particularly useful for those who wish to communicate effectively in social settings, travel, or work in the Levant region. Its adaptability and ease of use can significantly accelerate the learning process, making it a popular choice for Arabic language learners worldwide.
Cultural Significance
Levantine Arabic is deeply intertwined with the region’s culture and media. It’s the language of popular TV shows, films, and music that resonate across the Arab world. Artists like Fairuz and Marcel Khalife have immortalized the dialect in their timeless songs. This dialect, spoken in countries such as Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, and Palestine, serves as a unifying thread that connects people through shared cultural expressions. Whether it’s in the heartfelt lyrics of a song or the engaging dialogue of a TV drama, Levantine Arabic captures the essence of daily life and the collective experiences of its speakers. Its influence extends beyond entertainment, playing a crucial role in preserving the rich heritage and traditions of the Levantine people. From family gatherings where stories are passed down through generations to public celebrations that feature traditional music and dance, Levantine Arabic is a living testament to the region’s vibrant and enduring culture.
Literature in Levantine Arabic also holds a special place. Writers like Elias Khoury and Ghassan Kanafani have used the dialect to express profound stories of the Levantine experience, adding to its cultural richness. Khoury’s novels often explore themes of identity, memory, and loss, capturing the complexities of life in the region. Kanafani, a prominent Palestinian writer, delves into the struggles and resilience of the Palestinian people, offering powerful narratives that resonate deeply with readers. Their contributions have not only enriched Levantine literature but alsoprovided a voice to the socio-political issues of the area.
Variations Within Levantine Arabic
Dialectal Differences
Levantine Arabic is not a monolith; it varies significantly between Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, and Palestine. Lebanese Arabic is known for its French and English borrowings, adding a cosmopolitan flair to the dialect. Syrian Arabic, particularly the Damascus variety, is considered the most prestigious and widely understood.
Palestinian Arabic has its own set of unique features, influenced by its historical and cultural context. Jordanian Arabic,while closely related to Palestinian Arabic, incorporates Bedouin elements, making it distinct within the Levantine cluster.
Each sub-dialect offers a unique linguistic experience. Understanding these differences can enrich your learning and appreciation of Levantine Arabic.
Usage in Different Contexts
Levantine Arabic varies not only by region but also by context. Urban dialects, spoken in cities like Beirut, Damascus, and Amman, tend to be more influenced by foreign languages and modern expressions. Rural dialects, on the other hand, preserve more traditional elements.
Formal and informal usage also differs. In formal settings, speakers might incorporate more MSA elements, especially in business or academic environments. Informally, Levantine Arabic shines with its idiomatic expressions and colloquialisms, reflecting the warmth and hospitality of the region.
Why Learn Levantine Arabic?
Cultural Immersion
Learning Levantine Arabic offers an unparalleled opportunity to immerse yourself in the rich cultural heritage of the Levant. From savoring the intricate flavors of Levantine cuisine to enjoying traditional music and dance, the dialect opens doors to a deeper cultural understanding.
Access to cultural media is another significant benefit. Watching popular TV shows and movies in their original dialect, reading contemporary Levantine literature, and following local influencers on social media can enhance your language skills and cultural appreciation.
Travel and Communication
For travelers and expatriates, Levantine Arabic is invaluable. Whether you’re navigating the bustling streets of Beirut or exploring the ancient ruins of Petra, knowing the local dialect can enhance your experience. It allows you to connect with locals, understand cultural nuances, and make your travels more enriching.
Effective communication with locals in the Levantine region goes beyond transactional interactions. It builds relationships and fosters mutual respect, making your time in the region more enjoyable and meaningful.
Professional Opportunities
In today’s globalized world, proficiency in Levantine Arabic can open up numerous professional opportunities. Careersin translation, interpretation, and international relations benefit greatly from knowledge of this dialect.
For NGOs, diplomatic missions, and businesses operating in the Middle East, Levantine Arabic is a crucial asset. It enables better communication, deeper cultural understanding, and more effective relationship-building with local communities and stakeholders.
Tips for Learning Levantine Arabic
Learning Resources
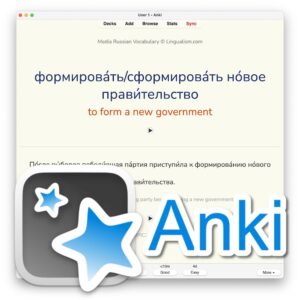
Starting your Levantine Arabic learning journey is easier with the right resources. eBooks and Anki flashcards by Lingualism offer structured lessons and interactive exercises to enhance your learning experience.
Practice and Immersion
Practical experience is key to mastering Levantine Arabic. Regular practice of speaking and listening skills can significantly improve your fluency. Engaging in language exchange programs, either online or within local communities, offers valuable practice opportunities.
Immersing yourself in the language environment is equally important. Watching Levantine Arabic TV shows, listening to regional music, and reading local news can enhance your understanding and appreciation of the dialect.
Cultural Experiences
Understanding the cultural context in which a language is used enhances language learning. Visiting cultural centers, attending Levantine festivals, and engaging with the local arts scene can provide a rich, immersive experience. Experiencing the culture firsthand helps in understanding the subtleties and nuances of the language, making communication more authentic and heartfelt.
Study Techniques
Effective study techniques can make a significant difference in your language learning progress. Building a robust vocabulary is essential; flashcards, spaced repetition systems (SRS), and mnemonic devices can help you retain new words and phrases.
Grammar practice is also crucial. Using workbooks and online exercises to practice sentence structures, verb conjugations, and common expressions can strengthen your grammatical foundation. Incorporating cultural studies into your learning process can provide context and deepen your understanding of the language.
Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Learning Levantine Arabic, like any language, comes with its challenges. Common difficulties include mastering pronunciation, understanding regional variations, and maintaining motivation. However, with consistent practice and the right strategies, these challenges can be overcome.
One effective strategy is to set small, achievable goals. This keeps you motivated and provides a sense of accomplishment as you progress. Joining a study group or finding a language partner can also provide support and encouragement.
Consistency is key. Regular practice, even if it’s just a few minutes a day, helps reinforce your learning and build confidence. Remember, language learning is a marathon, not a sprint.
Conclusion
Levantine Arabic is more than just a dialect; it is a vibrant reflection of the Levantine region’s rich history and culture. Learning Levantine Arabic offers numerous benefits, from cultural immersion and enhanced travel experiences to professional opportunities.
By understanding its unique features, variations, and cultural significance, you can appreciate the beauty and complexity of Levantine Arabic. With the right resources, practice, and study techniques, mastering this dialect is within your reach.
If you’re ready to start your Levantine Arabic learning journey, explore the resources mentioned in this guide. Immerse yourself in the language, practice regularly, and connect with the Levantine community. The rewards of learning Levantine Arabic are immense, enriching your understanding of the Middle East and opening up new opportunities for personal and professional growth.







Been studying Northern Palestinian Levantine Arabic for the past 11 yrs , loved it !